It
is almost as if Robertscribbler has discovered positive feedbacks for
the first time while Guy McPherson has identified 5 dozen posituve
and irreversible feedbacks. I had yet to see these countered
Beyond the Point of No Return — Imminent Carbon Feedbacks Just Made the Stakes for Global Warming a Hell of a Lot Higher
It
is almost as if Robertscribbler has discovered positive feedbacks for
the first time while Guy McPherson has identified 5 dozen posituve
and irreversible feedbacks. I had yet to see these countered
2
December, 2016
“It’s
fair to say we
have passed the point of no return on global
warming and
we can’t reverse the effects, but certainly we can dampen
them,” said
biodiversity expert Dr. Thomas Crowther.
“I’m
an optimist and still believe that it is not too late, but
we urgently need to develop a global economy driven by sustainable
energy sources and start using CO2, as a substrate,
instead of a waste product.” — Prof
Ivan Janssens,
recognized as a godfather of the global ecology field.
“…we
are at the most dangerous moment in the development of humanity. We
now have the technology to destroy the planet on which we live, but
have not yet developed the ability to escape it… we only have one
planet, and we need to work together to protect it.” — Professor
Stephen Hawking yesterday in The
Guardian.
*****
The
pathway for preventing catastrophic climate change just got a whole
hell of a lot narrower.
For
according to new, conservative estimates in
a scientific study led by Dr. Thomas Crowther,
increasing soil respiration alone is about to add between 0.45 and
0.71 parts per million of CO2 to the atmosphere every year between
now and 2050.
(Thomas
Crowther explains why rapidly reducing human greenhouse gas emissions
is so important. Namely, you want to do everything you can to avoid a
runaway into a hothouse environment that essentially occurs over just
one Century. Video source: Netherlands
Institute of Ecology.)
What
this means is that even if all of human fossil fuel emissions stop,
the Earth environment, from this single source, will generate about
the same carbon emission as all of the world’s fossil fuel industry
did during the middle of the 20th Century. And that, if human
emissions do not stop, then the pace of global warming of the oceans,
ice sheets, and atmosphere is set to accelerate in a runaway warming
event over the next 85 years.
Global
Warming Activates Soil Respiration Which Produces More CO2
This
happens because as the world warms, carbon is baked out of previously
inactive soils through a process
known as respiration. As a basic explanation, micro-organisms called heterotrophs consume carbon in the soil and produce carbon dioxide as a bi-product. Warmth is required to fuel this process. And large sections of the world that were previously too cold to support large scale respiration and CO2 production by heterotrophs and other organisms are now warming up. The result is that places like Siberian Russia, Northern Europe, Canada, and Alaska are about to contribute a whole hell of a lot more CO2 (and methane) to the atmosphere than they did during the 20th Century.
known as respiration. As a basic explanation, micro-organisms called heterotrophs consume carbon in the soil and produce carbon dioxide as a bi-product. Warmth is required to fuel this process. And large sections of the world that were previously too cold to support large scale respiration and CO2 production by heterotrophs and other organisms are now warming up. The result is that places like Siberian Russia, Northern Europe, Canada, and Alaska are about to contribute a whole hell of a lot more CO2 (and methane) to the atmosphere than they did during the 20th Century.
When
initial warming caused by fossil fuel burning pumps more carbon out
of the global environment, we call this an
amplifying feedback.
It’s a critical climate tipping point when the global carbon system
in the natural environment starts to run away from us.
Sadly,
soil respiration is just one potential feedback mechanism that can
produce added greenhouse gasses as the Earth warms. Warming oceans
take in less carbon and are capable of producing their own carbon
sources as they acidify and as methane seeps proliferate. Forests
that burn due to heat and drought produce their own carbon sources.
But increasing soil respiration, which
has also been called the compost bomb,
represents what is probably one of the most immediate and likely
large sources of carbon feedback.
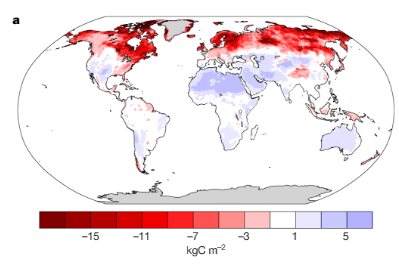 (A
new study finds that warming of 1 to 2 C by 2050 will increase soil
respiration. The result is that between 30 and 55 billion tons of
additional CO2 is likely to hit the Earth’s atmosphere over the
next 35 years. Image source: Nature.)
(A
new study finds that warming of 1 to 2 C by 2050 will increase soil
respiration. The result is that between 30 and 55 billion tons of
additional CO2 is likely to hit the Earth’s atmosphere over the
next 35 years. Image source: Nature.)
And
it is also worth noting that the
study categorizes
its own findings as conservative estimates. That the world could, as
an outside risk, see as much as four times the amount of carbon
feedback (or as much as 2.7 ppm of CO2 per year) coming from soil if
respiration is more efficient and wide-ranging than expected. If a
larger portion of the surface soil carbon in newly warmed regions
becomes a part of the climate system as microbes activate.
Amplifying
Feedbacks Starting to Happen Now
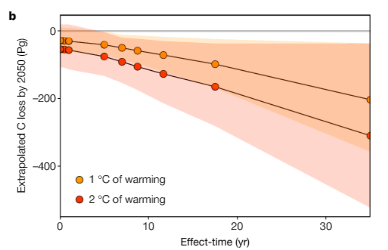
The
study notes
that it is most likely that about 0.45 parts per million of CO2 will
be leached from mostly northern soils from the period of 2016 to 2050
under 1 C worth of global warming during the period. To this point,
it’s worth noting that the world has already warmed by more than 1
C above preindustrial levels. So this amount of carbon feedback can
already be considered locked in. The study finds that if the world
continues to warm to 2 C by 2050 — which is likely to happen —
then an average of around 0.71 parts per million of CO2 will be
leached out of soils by respiration every year through 2050.

(When
soils lose carbon, it ends up in the atmosphere. According to a new
study, soils around the world are starting to pump carbon dioxide
into the atmosphere. This is caused by increased soil respiration as
the Earth warms. Over the next 35 years, the amount of carbon dioxide
being pumped out by the world’s soils is expected to dramatically
increase. How much is determined by how warm the world becomes over
the next 35 years. Image source: Nature.)
The
upshot of this study is that amplifying carbon feedbacks from the
Earth environment are probably starting to happen on a large scale
now. And we may be seeing some evidence for this effect during 2016
as rates of atmospheric carbon dioxide accumulation are hitting
above 3
parts per million per year for the second year in a row even
as global rates of human emissions plateaued.
Beyond
the Point of No Return
What
this means is that the stakes for cutting human carbon emissions to
zero as swiftly as possible just got a whole hell of a lot higher. If
we fail to do this, we will easily be on track for 5-7 C or worse
warming by the end of this Century. And this level of warming
happening so soon and over so short a timeframe is an event that few,
if any, current human civilizations are likely to survive.
Furthermore, if we are to avoid terribly harmful warming over longer
periods, we must not only rapidly transition to renewable energy
sources. We must also somehow learn to pull carbon, on net, out of
the atmosphere in rather high volumes.
“This study is very important, because the response of soil carbon stocks to the ongoing warming, is one of the largest sources of uncertainty in our climate models. I’m an optimist and still believe that it is not too late, but we urgently need to develop a global economy driven by sustainable energy sources and start using CO2, as a substrate, instead of a waste product. If this happens by 2050, then we can avoid warming above 2C. If not, we will reach a point of no return and will probably exceed 5C.”
In
other words, even the optimists at this time think that we are on the
cusp of runaway catastrophic global warming. That the time to
urgently act is now.
Links:
Hat
tip to TodaysGuestIs
Hat
tip to Cate
Hat
tip to Colorado Bob



No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.