Arctic
Sea Ice Extent at Record Lows as Winter Temperatures Soar
12
February 2018
That’s
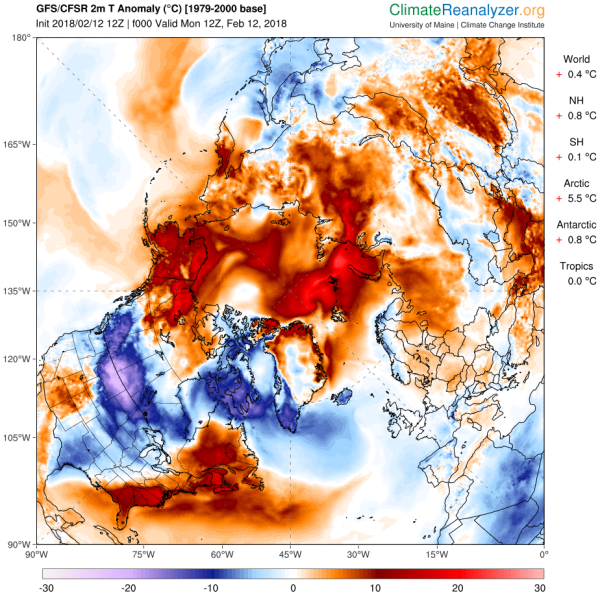
how much warmer than ‘normal’ the entire region of the Arctic
above the 66 degree North Latitude Line was earlier today. Areas
within this large warm pool saw temperatures spike to a range of 15
to 25 C warmer than the already warmer than normal 1981-2010 base
period. And broad regions saw temperature between 10 and 20 C above
that 30-year average.
(The
entire Arctic is an incredible 5.5 C warmer than normal today.
Meanwhile, Arctic sea ice extent has plunged, once-more, into record
low ranges. Image source: Climate
Reanalyzer.)
It’s
just a snapshot. But
day after day, week after week, month after month, the story has been
much the same throughout Fall and Winter of 2017-2018.
And
as during last year’s ridiculously warm Arctic winter, the sea ice
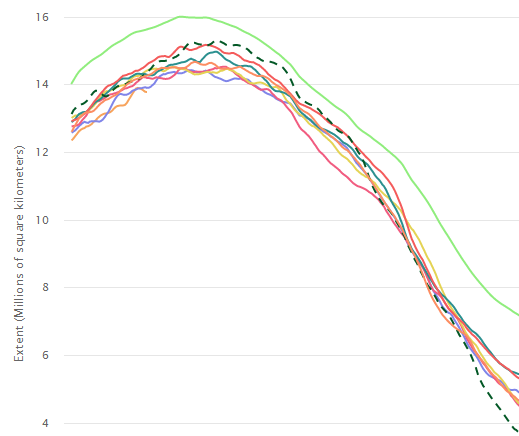
has taken a considerable pounding. Yesterday
dropping to a new record low extent of 13.774 million square
kilometers.
Beating out the previous record low for the day set just last year.
And dipping more than 1.8 million square kilometers below the
1979-1990 average. A period that already featured greatly reduced
Arctic sea ice cover when compared to extents seen in the early 20th
Century.
(Arctic
sea ice extent for 2018 [lower pink line above] dipped into new
record low ranges during recent days. Note that the 1979 – 1990
extent average is indicated by the green line at top. Image
source: NSIDC.)
The
primary cause of these ice losses is warming both of the ocean and of
the air. And, as we can see in the ongoing trend, the Arctic is
getting more than its fair share of both. Such
polar amplification is a direct upshot of the massive volume of
harmful greenhouse gasses being injected into the atmosphere through
fossil fuel burning.
And we are seeing the dark fruits of that burning now in the massive
and ongoing winter losses of sea ice, the harm to various Arctic life
forms like puffins and polar bears, and the risk of increasing sea
level rise, ocean circulation destabilization, and increasingly
extreme weather events that all result from the heating-up of polar
environments.



No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.