This is just to remind us of what is most important – and it’s not a stolen election
Hot Climate Conjures Trio of Nasty Halloween Tricks — Heatwaves, Record-Low Sea Ice, Fall Greenland Melt
31
October, 2016
With
each passing year, the effects of human-caused climate change become
more and more visible. But for some reason, Halloween appears to be a
preferred time for the emergence of various hothouse hobgoblins.
In 2012, the Atlantic seaboard was reeling after a vicious
strike from Hurricane Sandy. Over the past three years, powerful
North Atlantic storms had begun to build at this time of year,
setting sights on the UK and Europe. This year, as
a hurricane-force low roars toward the Aleutians,
the nastiness comes in the form of weird heatwaves, record-low global
sea ice coverage, and hints of odd late-fall Greenland melt.
Record
Heat Strikes Arctic, U.S.
NASA’s
Gavin Schmidt has been warning for months that 2016 will be a global
scorcher for the record books.
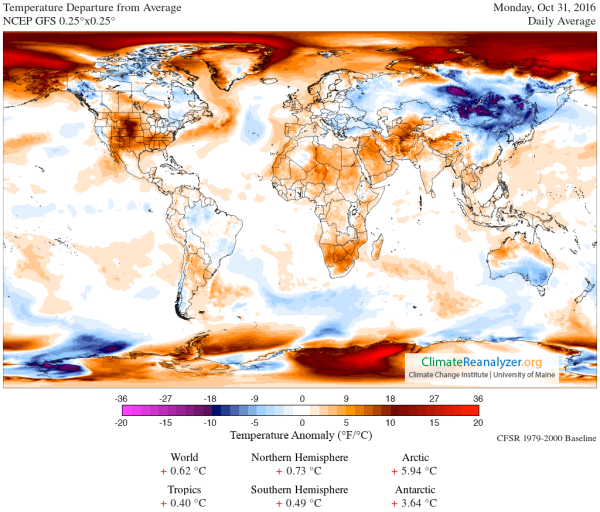
Nowhere has this heat been more apparent than in the Arctic.
Halloween only serves to reinforce the rule as today’s temperature
departure for the entire region above 66 degrees north latitude hit
5.94 degrees Celsius above average:
(The
extreme Arctic warmth that has already caused so much in the way of
climate disruption remains firmly entrenched on Halloween. Image
source: Climate
Reanalyzer.)
Yesterday,
those temperatures exceeded the 6-C-above-normal mark. And later this
week, temperatures for the region could approach 6.3 to 6.5 C above
average.
These
are the average departure ranges for the entire area above the Arctic
Circle. Localities within that broader region are hitting as
much as 20 C (36 Fahrenheit) or more above average on an almost daily
basis, bringing temperatures more typical of the Arctic during late
summer than in the middle of fall.
In
Barrow, Alaska, Jonathan
Erdman reports that Saturday saw the proverbial mercury hit 41 F.
This temperature, at about 26 degrees above average, smashed the
previous daily high and pushed the latest day Barrow has ever seen a
reading above 40 F fully one week forward.
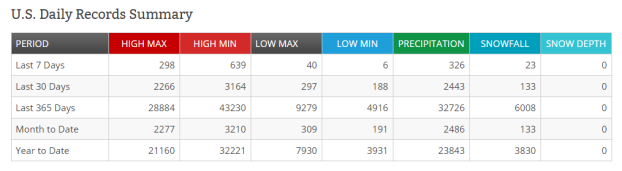
(Daily
high and high min temperature records for the U.S. were broken at an
alarming rate over the past week, producing a Halloween heatwave.
Image source: NOAA.)
Farther
south, the lower 48 is experiencing what Bob
Henson over at Weather Underground is calling the Halloween Heatwave.
Over the past week alone, nearly 300 daytime high marks were broken.
But the measure of record-high minimum temperatures — a key
indicator of human-forced warming — is off the charts with 639
total records smashed over the past seven days.
Even more noteworthy than the degree of warmth is the lack of widespread autumn chill. For example, Minneapolis has yet to dip below 36°F as of Friday, October 28. That doesn’t look likely to happen before at least next weekend (November 5 – 6). In records going back to 1873, the latest Minneapolis has ever gone before seeing its first 35°F of the autumn is November 1, way back in 1931. The city’s latest first freezewas on Nov. 7, 1900.
Reinforcing
this point, NOAA
finds that over the past week just 40 record low high temperatures
were achieved (about
one-seventh the number of record highs). Meanwhile, record low
nighttime temperatures were only achieved in six instances, about
one-one-hundredth the rate of record high minimum temperatures!
Furthermore, at no location in the U.S. for this week, this month, or
even this past year has snow depth achieved a new record high. That’s
a pretty ridiculous indicator that the U.S. has reached a rather
disturbing climate threshold for heat overall.
Record
Low Global Sea Ice Coverage
Even
as new warm temperature records were being set with amazing frequency
across parts of the Northern Hemisphere, another duo of worrisome
indicators were popping up in the Arctic and Antarctic. In the
Arctic, the ocean has been loaded up with a ridiculous amount of
heat. This heat is preventing the ocean from refreezing, creating
various regional barriers to ice formation as the waters ventilate
this excess heat into the atmosphere. As a result, Arctic sea-ice
extent record lows continue to deepen.
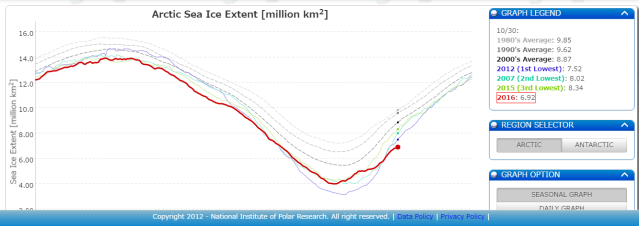
Fall
2016 sea ice extent values — which have consistently lagged behind
average daily refreeze rates for most of the season — are now more
than 600,000 square kilometers below the previous record set during
2012. It’s, quite frankly, an insane shattering of the previous
record low value; a warming-spurred melt that has erased an area of
sea ice coverage nearly the size of Texas in just four years.
(Current
Arctic sea ice extent values are 6.92 million square kilometers
[October 30]. This is 600,000 square kilometers below the previous
record low set on the same day during 2012. It is also about 3
million square kilometers below average values seen for this day back
during the 1980s. Image source: JAXA.)
The
Washington Post this past Friday provided a
good article explaining the dynamics involved and
highlighted predictions by prominent Arctic researchers that ice-free
summers could occur by the 2030s. This is a marked departure from
earlier estimates that had put off ice-free summers until the 2050s
or even the 2080s. However, it’s worth noting that there’s a
decent risk that even these more advanced predictions may prove
conservative in the end. Under current trends, ice-free periods for
the Arctic Ocean during summer become statistically possible as soon
as the early to mid 2020s, and a strong outlier year — where an
abnormally warm winter is followed by an abnormally warm summer —
could produce such a result even sooner.
On
the other side of the world, the Antarctic is also experiencing
record-low ranges for sea ice extents. There, regional
temperatures are near 4 C above average for the entire Antarctic.
Though these departures are not as extreme as those currently seen in
the Arctic, they are certainly enough to impact sea ice. Now,
sea ice extent values there are at their second lowest ever recorded
in the daily measure.
Over
recent years, storminess in the Southern Ocean and an expanding fresh
water lens running out from Antarctica due to glacial melt have
generated a seemingly contradictory expansion of sea ice near
Antarctica. This happens because fresh water at the ocean’s surface
acts to deflect heat toward the ocean bottom, a
feature that has enabled the melting of various glacier undersides in
Antarctica.
But as the global ocean and atmosphere warm in general, larger melt
outflows are necessary to reinforce this surface freshwater lens
effect. As a result, we appear to be experiencing a seesaw in
Antarctic sea ice extent as a pulse of atmospheric and ocean warming
overrides the impact of initial fresh water lensing.
(MASIE
global sea ice extent shows a severe negative departure through
October 28, 2016. Image source: Sunshine Horus.)
The
combination of significant sea ice losses in the north and
second-lowest sea ice extents in the south has resulted in a global
sea-ice measure that is well below anything seen in the past for this
time of year. It is also one of the largest global negative sea-ice
departures seen for any part of the record for any time of year —
even when compared to the extreme period of Arctic sea ice loss
during September of 2012.
Halloween
Greenland Melt?
In
addition to producing heatwaves, new temperature records, and ever
more extreme sea ice melt, the odd Halloween warmth appears to also
be generating flashes of surface melt over parts of northeastern
Greenland. There, over the past few days, temperatures have
approached or even exceeded the freezing point as warm winds have
blown in from the heating Greenland Strait.
(A
warm front crosses over northeastern Greenland on October 27, 2016.
The associated warm winds blowing off the heating waters of the
Greenland Strait produced near or above freezing temperatures for
isolated parts of this section of Greenland. This abnormal warmth
appears to have tripped NSIDC’s melt sensor, producing a possible
odd late-season melt event for sections of this frozen island. Image
source: Earth
Nullschool.)
This
heat has been enough to trip NSIDC’s
Greenland melt indicators for
the region of the Zachariæ
Isstrøm glacier.
These indicators, over the past couple of days, have shown relatively
extensive melt in this sector of Greenland. During summer 2016,
northeastern Greenland was one of the regions that saw strongest
indications of surface melt. Typically isolated by sea ice from warm
ocean breezes, northeast Greenland does not usually see such
long-lasting periods of surface melt. This is especially true for
late October as melt during this time for any portion of the
Greenland Ice Sheet is practically unheard of. However, as warm
ocean water has advanced further and further north, this region has
become more vulnerable to invasions of warm air. And it appears that
the melt-forcing effect of this ocean warming for nearby Greenland
glaciers may well be extending into all.
Though
unconfirmed by NSIDC, these periods of possible melt have occurred
coincident with temperature departures in the range of 10-20 degrees
C above average. However, since near or above freezing temperatures
have mostly been isolated to the very far northeastern sections
of Zachariæ Isstrøm near the coast, it’s likely that any
potential and brief periods of melt were located in a more limited
band than what has shown up on the NSIDC
melt maps for October 27, 28, and 29.
That said, as noted above, any surface melt over glaicers in
Greenland for this time of year would be very odd and concerning —
no matter how isolated.
Nasty
Global Warming Tricks for Halloween
Halloween
heatwaves, record-low sea ice extents and possible periods of fall
Greenland melt are all indicators that human-forced climate change is
starting to generate more and more obvious effects. Though the most
extreme impacts are hitting remote regions like Greenland, the Arctic
and the Antarctic, the related abnormal warmth has filtered into the
middle latitudes and is now affecting millions of people across the
U.S. And what’s happening in the U.S. is linked to these related
warming events on a global scale.
So
happy Halloween, everyone. Enjoy the holiday. But remember that if
it’s oddly warm where you are, it’s not just a freak warm weather
treat, but one of the many and worsening tricks conjured up by global
climate change.
Links:
Hat
tip to Colorado Bob
Hat
tip to DT Lange
Hat
tip to June





No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.