Rural
America Is On The Verge Of Collapse
24 May, 2019
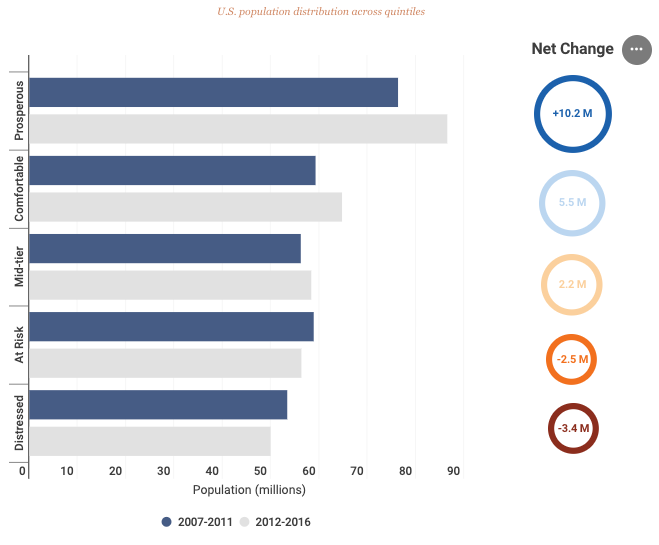
The Economic Innovation Group's (EIG) Distressed Communities Index (DCI) shows a significant economic transformation (from two distinct periods: 2007-2011 and 2012-2016) that occurred since the financial crisis. The shift of human capital, job creation, and business formation to metropolitan areas reveals that rural America is teetering on the edge of collapse.
Since the crisis, the number of people living in prosperous zip codes expanded by 10.2 million, to a total of 86.5 million, an increase that was much greater than any other social class. Meanwhile, the number of Americans living in distressed zip codes decreased to 3.4 million, to a total of 50 million, the smallest shift of any other social class. This indicates that the geography of economic pain is in rural America.
"While the overall population in distressed zip codes declined, the number of rural Americans in that category increased by nearly 1 million between the two periods. Rural zip codes exhibited the most volatility and were by far the most likely to be downwardly mobile on the index, with 30 percent dropping into a lower quintile of prosperity—nearly twice the proportion of urban zip codes that fell into a lower quintile. Meanwhile, suburban communities registered the greatest stability, with 61 percent remaining in the same quintile over both periods. Urban zip codes were the most robust—least likely to decline and more likely than their suburban counterparts to rise," the report said.
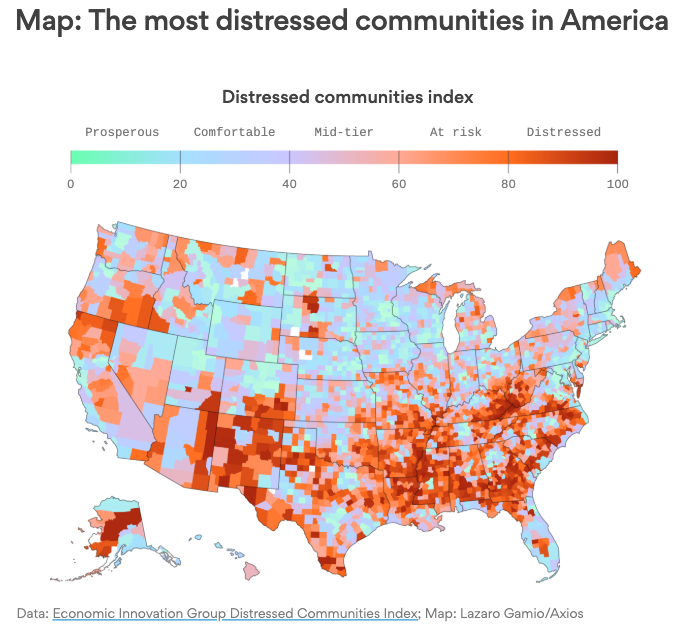
Visualizing the collapse: Economic distress was mostly centered in the Southeast, Rust Belt, and South Central. In Alabama, Arkansas, Mississippi, and West Virginia, at least one-third of the population were located in distressed zip codes.
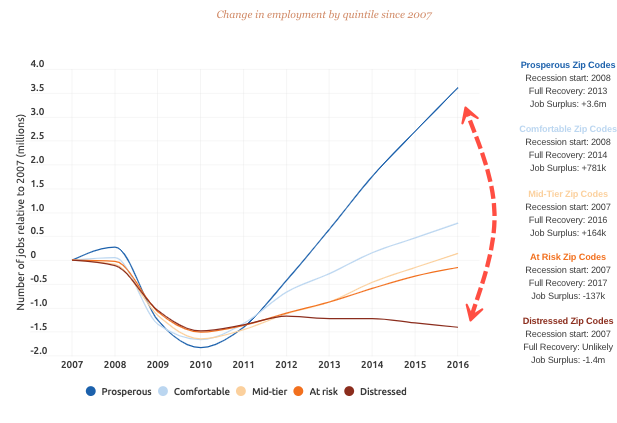
Prosperous zip codes were the top beneficiaries of the jobs recovery since the financial crisis. All zip codes saw job declines during the recession, each laying off several million jobs from 2007 to 2010. But by 2016, prosperous zip codes had 3.6 million jobs surplus over 2007 levels, which was more than the bottom 80% of distressed zip codes combined. It took five years for prosperous zip codes to replace all jobs lost from the financial crisis; meanwhile, distressed zip codes will never recover.
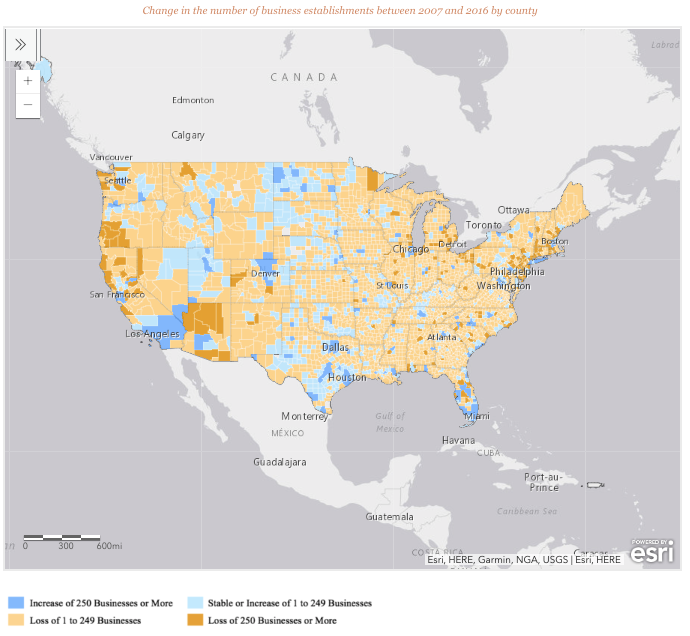
EIG shows that less than 25% of all counties have recovered from business closures from the recession.
"US business formation has been dismal in both magnitude and distribution since the Great Recession. The country's population is almost evenly split between counties that have fully replaced (with 161 million residents) and those that have not (with 157.4 million). This divide is due to the fact that highly populous counties—those with more than 500,000 residents—were far more likely to add businesses above and beyond 2007 levels than their smaller peers. Nearly three in every five large counties added businesses on net over the period, compared to only one in every five small one," the report said.
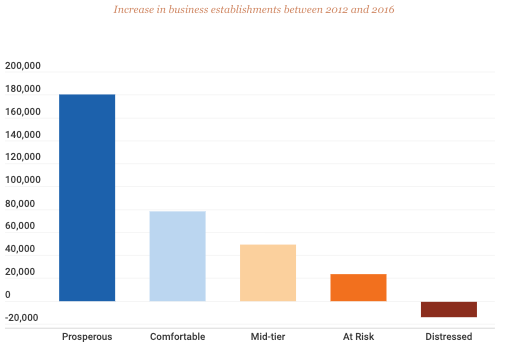
To highlight the weak recovery and geographic unevenness of new business formation, EIG shows that the entire country had 52,800 more business establishments in 2016 than it did in 2007.
Five counties (Los Angeles, CA; Brooklyn, NY; Harris, TX (Houston); Queens, NY; and Miami-Dade, FL. ) had a combined 55,500 more businesses in 2016 than before the recession. Without those five counties, the US economy would not have recovered.
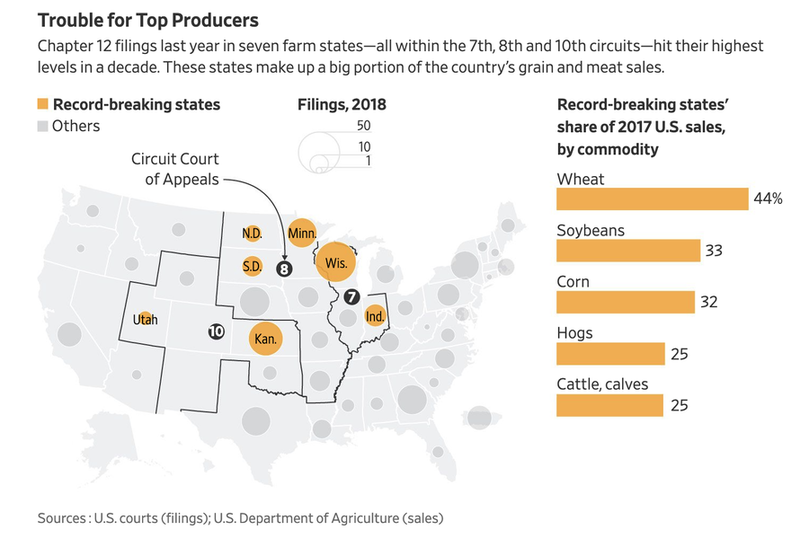
On top of deep structural changes in rural America, JPMorgan told clients last week that the entire agriculture complex is on the verge of disaster, with farmers in rural America caught in the crossfire of an escalating trade war.
"Overall, this is a perfect storm for US farmers," JPMorgan analyst Ann Duignan warned investors.
Farmers are facing tremendous headwinds, including a worsening trade war, collapsing soybean exports to China, global oversupply conditions, and crop yield losses in the Midwest due to flooding. This all comes at a time when farmers are defaulting and missing payments at alarming rates, forcing regional banks to restructure and refinance existing loans.
Today's downturn of rural America is no different than what happened in the 1920s, 1930s, and the early 1980s.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.